|
EIP Differentiated based on its works. Reference : EIP |
Saturday, July 25, 2015
EIP : Enterprise Integration Patterns
Apache Camel: Splitter Component And Aggregation EIP
Today, I'm going to explain about the Camel's Splitter component. I will also explain how and when to use this component. Here, I used Spring DSL to configure the splitter. So, let's start the camel riding.
The splitter component is based on Splitter EIP which allows you to split your incoming message into no. of smaller pieces and process them independently. It's considered as parallel processing of bulk messages which comes as a single bundled. The splitted message will be set as a body of message in newly created exchange which contains all the headers, properties of parent exchange. This component supports various data types including xml, json, csv, etc. This is about when to use this component.
There are various options available for this component which you can configure in spring dsl by setting respective attributes along with its value to make it more powerful route. Along with Splitter component I will also explain about the Aggregation EIP. The aggregation EIP is used to collect output from parallelly processed splitted messages. I think this is sufficient explanation for Splitter component. You can read from official Apache Camel website.
Now, Let's start the programming. I assume that you have created your project by using Maven.
<!-- This bean is used to collect the output from the splitted messages from splitter component -->
<bean id="aggregationBean" class="com.makhir.beans.AggregationStrategyBean" />
<camel:route id="SplitterExampleRoute">
<camel:from uri="direct:SplitterExampleRoute" />
<camel:log logName="SplitterExampleRoute" loggingLevel="INFO"
message="Entered in Splitter Component : ${body}" />
<camel:split strategyRef="aggregationBean" stopOnException="false">
<camel:xpath>//Orders/Order</camel:xpath>
<camel:to uri="direct:SplittedMessageProcessingRoute" />
</camel:split>
</camel:route>
<camel:route id="SplittedMessageProcessingRoute">
<camel:from uri="direct:SplittedMessageProcessingRoute" />
<camel:log logName="SplittedMessageProcessingRoute" loggingLevel="INFO"
message="Entered in SplittedMessageProcessingRoute : ${body}" />
<!--
Add your business logic for validation, transformation, etc.
-->
<camel:to uri="direct:some-route"/>
</camel:route>
package com.makhir.beans;
import org.apache.camel.Exchange;
import org.apache.camel.processor.aggregate.AggregationStrategy;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class AggregationStrategyBean implements AggregationStrategy {
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AggregationStrategyBean.class);
@Override
public Exchange aggregate(Exchange oldExchange, Exchange newExchange) {
try {
if (oldExchange == null || oldExchange.getIn() == null
|| oldExchange.getIn().getBody() == null
|| oldExchange.getIn().getBody(String.class) == null) {
checkAndProcessExchange(newExchange);
return newExchange;
} else if (newExchange == null || newExchange.getIn() == null
|| newExchange.getIn().getBody() == null
|| newExchange.getIn().getBody(String.class) == null) {
return oldExchange;
}
//Add your business logic for capturing the information from the splitted message(newExchange)
//and set it into parent message(oldExchange)
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("There was a problem while aggregating the data, error message " + e.getMessage());
}
return oldExchange;
}
}
That's it. You can try this by adding above routes in your camel context as per your requirement.
I hope you have enjoyed this camel ride.
Reference: Apache Camel
The splitter component is based on Splitter EIP which allows you to split your incoming message into no. of smaller pieces and process them independently. It's considered as parallel processing of bulk messages which comes as a single bundled. The splitted message will be set as a body of message in newly created exchange which contains all the headers, properties of parent exchange. This component supports various data types including xml, json, csv, etc. This is about when to use this component.
There are various options available for this component which you can configure in spring dsl by setting respective attributes along with its value to make it more powerful route. Along with Splitter component I will also explain about the Aggregation EIP. The aggregation EIP is used to collect output from parallelly processed splitted messages. I think this is sufficient explanation for Splitter component. You can read from official Apache Camel website.
Now, Let's start the programming. I assume that you have created your project by using Maven.
<!-- Incoming XML -->
<Orders>
<Order>
<Header>...</Header>
<LineItems>
<LineItem>...</LineItem>
</LineItems>
<Footer>...</Footer>
</Order>
.
.
.
<Order>
<Header>...</Header>
<LineItems>
<LineItem>...</LineItem>
</LineItems>
<Footer>...</Footer>
</Order>
</Orders>
Now, Sping DSL for Splitter Copmonent,
<bean id="aggregationBean" class="com.makhir.beans.AggregationStrategyBean" />
<camel:route id="SplitterExampleRoute">
<camel:from uri="direct:SplitterExampleRoute" />
<camel:log logName="SplitterExampleRoute" loggingLevel="INFO"
message="Entered in Splitter Component : ${body}" />
<camel:split strategyRef="aggregationBean" stopOnException="false">
<camel:xpath>//Orders/Order</camel:xpath>
<camel:to uri="direct:SplittedMessageProcessingRoute" />
</camel:split>
</camel:route>
<camel:route id="SplittedMessageProcessingRoute">
<camel:from uri="direct:SplittedMessageProcessingRoute" />
<camel:log logName="SplittedMessageProcessingRoute" loggingLevel="INFO"
message="Entered in SplittedMessageProcessingRoute : ${body}" />
<!--
Add your business logic for validation, transformation, etc.
-->
<camel:to uri="direct:some-route"/>
</camel:route>
Now, I'm writing the aggregation class which is as per below,
import org.apache.camel.Exchange;
import org.apache.camel.processor.aggregate.AggregationStrategy;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class AggregationStrategyBean implements AggregationStrategy {
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AggregationStrategyBean.class);
@Override
public Exchange aggregate(Exchange oldExchange, Exchange newExchange) {
try {
if (oldExchange == null || oldExchange.getIn() == null
|| oldExchange.getIn().getBody() == null
|| oldExchange.getIn().getBody(String.class) == null) {
checkAndProcessExchange(newExchange);
return newExchange;
} else if (newExchange == null || newExchange.getIn() == null
|| newExchange.getIn().getBody() == null
|| newExchange.getIn().getBody(String.class) == null) {
return oldExchange;
}
//Add your business logic for capturing the information from the splitted message(newExchange)
//and set it into parent message(oldExchange)
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("There was a problem while aggregating the data, error message " + e.getMessage());
}
return oldExchange;
}
}
That's it. You can try this by adding above routes in your camel context as per your requirement.
I hope you have enjoyed this camel ride.
Reference: Apache Camel
Monday, June 22, 2015
Apache Camel: Jetty Component
Today, I'm going to explain about the Camel's Jetty component and how to configure to the jetty component. Here, I used Spring DSL to configure the jetty component. So, let's start the camel riding.
Camel's jetty component is used for HTTP/S based request/response as like classical Servlet. Jetty component consumes and produces the http request/response and support GET, POST, DELTE, PUT methods of forms. It act as a servlet as we define J2EE web project. It receive the request from the client, process it and create the response accordingly. With Jetty component we can create the HTTP based endpoints which consumes/produces http request.
Now, Let's start the programming. I assume that you have created your project by using Maven. I also assume that you have added all the dependency required for camel in your project.
Add the below dependency in your project's pom.xml
Now, I'm going to add the endpoints which receive the incoming request and respond it accordingly. Below is the configuration based on Spring DSL.
The Spring-DSL for camel-jetty component,
<!-- Jetty Component -->
<camel:route id="httpComponent" startupOrder="1">
<camel:from uri="jetty:http://URL:PORT/makhir?continuationTimeout=100000" />
<camel:setExchangePattern pattern="InOut" />
<camel:convertBodyTo type="java.lang.String" charset="UTF-8"/>
<camel:to uri="log:Recived Input in httpComponent?showAll=true" />
<camel:choice>
<camel:when>
<camel:simple>${header.CamelHttpMethod} == "GET"</camel:simple>
<camel:to uri="direct:testGetRoute" />
</camel:when>
<camel:when>
<camel:simple>${header.CamelHttpMethod} == "POST"</camel:simple>
<camel:to uri="direct:splitterRoute" />
</camel:when>
</camel:choice>
</camel:route>
We can have same component using Java DSL also. I've created the jetty component which receives the incoming http request and serve accordingly as per below.
Now, you should add this routes in your main class which have CamelContext object. About how to add the routes in camelcontext I've explained in my first blog related to camel.
That's it. Now build your project and deployed it in your ESB and try to call that endpoint by creating some java test class using http client.
You can use the Jetty component as per your need in your application. It gives web servlet like features in camel routing.
You can read more about camel:jetty component Apache Camel.
Hope, you have enjoyed this camel ride.
Camel's jetty component is used for HTTP/S based request/response as like classical Servlet. Jetty component consumes and produces the http request/response and support GET, POST, DELTE, PUT methods of forms. It act as a servlet as we define J2EE web project. It receive the request from the client, process it and create the response accordingly. With Jetty component we can create the HTTP based endpoints which consumes/produces http request.
Now, Let's start the programming. I assume that you have created your project by using Maven. I also assume that you have added all the dependency required for camel in your project.
Add the below dependency in your project's pom.xml
<dependency>After adding jetty dependency please do clean and build your project.
<groupId>org.apache.camel</groupId>
<artifactId>camel-jetty</artifactId>
<version>X.X.X</version> <!-- Here, the version must be same as your project's camel version -->
</dependency>
Now, I'm going to add the endpoints which receive the incoming request and respond it accordingly. Below is the configuration based on Spring DSL.
The Spring-DSL for camel-jetty component,
<!-- Jetty Component -->
<camel:route id="httpComponent" startupOrder="1">
<camel:from uri="jetty:http://URL:PORT/makhir?continuationTimeout=100000" />
<camel:setExchangePattern pattern="InOut" />
<camel:convertBodyTo type="java.lang.String" charset="UTF-8"/>
<camel:to uri="log:Recived Input in httpComponent?showAll=true" />
<camel:choice>
<camel:when>
<camel:simple>${header.CamelHttpMethod} == "GET"</camel:simple>
<camel:to uri="direct:testGetRoute" />
</camel:when>
<camel:when>
<camel:simple>${header.CamelHttpMethod} == "POST"</camel:simple>
<camel:to uri="direct:splitterRoute" />
</camel:when>
</camel:choice>
</camel:route>
We can have same component using Java DSL also. I've created the jetty component which receives the incoming http request and serve accordingly as per below.
/**
* This is the jetty component which creates the http endpoint which
* consumes the http request and respond accordingly.
* @author Ashish Mishra
* @since 22-06-2015 15:02:05
* */
public class JettyCommponent extends RouteBuilder{
@Override
public void configure() throws Exception {
from("jetty:http://localhost:8080/makhir?continuationTimeout=100000").process(
new Processor() {
@Override
public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception {
String message = exchange.getIn().getBody(String.class);
System.out.println("Request Body Message : " + message);
String httpMethod = (String) exchange.getProperty("CamelHttpMethod");
System.out.println("Http Method : " + httpMethod);
if(httpMethod.equalsIgnoreCase("GET")){
System.out.println("Add implementation for GET method and route accordingly");
} else if(httpMethod.equalsIgnoreCase("POST")){
System.out.println("Add implementation for POST method and route accordingly");
} else
System.out.println("Default Implementation " + message);
exchange.getOut().setBody("Response: " + message);
}
});
}
}
Now, you should add this routes in your main class which have CamelContext object. About how to add the routes in camelcontext I've explained in my first blog related to camel.
That's it. Now build your project and deployed it in your ESB and try to call that endpoint by creating some java test class using http client.
You can use the Jetty component as per your need in your application. It gives web servlet like features in camel routing.
You can read more about camel:jetty component Apache Camel.
Hope, you have enjoyed this camel ride.
Wednesday, April 15, 2015
Apche Camel : First Step Towards
Here, I'm going to explain basic things of Apache Camel which is an open source project from Apache Foundation. At the end we will see the simple example which demonstrate the FileComponent of Apche Camel.
To go further I assumed that you have enough knowledge of EIP(Enterprise Integration Patterns), MEP(Message Exchange Patterns), DSL(Domain Specific Languages), ESB, etc. It is advised to have basic information of above mentioned terms before you read further.
Now a days data becoming crucial things in the Cyber World among all the companies. To exchange the data between them is more crucial as each company has their own system to handle this data. It is important to have technology which fills this gap in such a way that exchange of data among companies accurately, efficiently, speedily, reliably, securely and off course easily. There are many open source solutions available to fill this gap. But I found Apache Camel is most preferable open source solution for integrating different systems to exchange the data in a different format. I became a camel lover since when I started using it and off-course because it is written in Java.
Now, I think this is enough for you about why Apache Camel is useful. Let's start with the Apache Camel architecture.
To go further I assumed that you have enough knowledge of EIP(Enterprise Integration Patterns), MEP(Message Exchange Patterns), DSL(Domain Specific Languages), ESB, etc. It is advised to have basic information of above mentioned terms before you read further.
Now a days data becoming crucial things in the Cyber World among all the companies. To exchange the data between them is more crucial as each company has their own system to handle this data. It is important to have technology which fills this gap in such a way that exchange of data among companies accurately, efficiently, speedily, reliably, securely and off course easily. There are many open source solutions available to fill this gap. But I found Apache Camel is most preferable open source solution for integrating different systems to exchange the data in a different format. I became a camel lover since when I started using it and off-course because it is written in Java.
Now, I think this is enough for you about why Apache Camel is useful. Let's start with the Apache Camel architecture.
Now let's see the key concept or components which make Apache Camel a powerful integration and routing framework among all the available in the same category.
- Camel Context: Camel Context is the heart of the Camel Framework. It's runtime environment where different entity communicate with each other. For more you can see the lifecyle of CamelContext in detail
- Camel Endpoints: Camel Endpoints are nothing but the Message Endpoints which is based on EIP by using Endpoint interface. Camle can receive messages from Endpoints or send messages to the Endpoints. You can read more on EIP by visiting this http://www.enterpriseintegrationpatterns.com
- Camel Processors: Processors are the again key entity in camel which is associated with processing of incoming messages from Endpoints. For more you can visit http://camel.apache.org/processor.html
- Camel Components: Camel Components defined the Endpoint in message lifecyle in camel. There are more than 80 components available in the camel. You can refer them on official camel website. http://camel.apache.org/components.html
- Camel Route: Camel Route are the flow of the message. How it process in camel. It has two endpoints associated with it and respectively Camel component as well. Camel route also having the filter, interceptor, validator, converter which defined the flow of the message. We can create a route via DSL. There are different DSL available which defined the route of the message. Most commonly used are Spring DSL, Java DSL. You can read more on that by your own as it's a very huge topic and we are not going elaborate them over here.
Now, I'm winding up theoretical part as you can read whenever you want from the net. I knew that you are quite interested in the programming. :D :D :D
So, Let's begin that. First you need to download the Apache Camel from the official site. You can download form here.
I will be surprised if you don't have java installed on your machine and you are not using any of the popular IDE for doing programming. If you do not have java than please make java available on your machine.
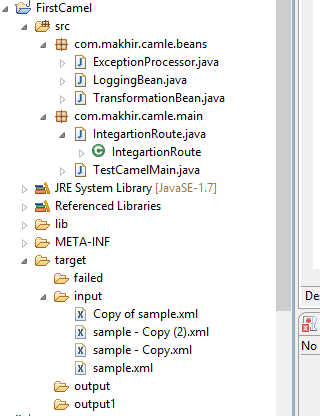
Now, create on java project. Here, I've used Eclipse IDE for my stuffs. Below is the directory structure.
Add the required jar in the lib folder of your project from the downloaded Apache Camel zip file after extraction on you local drive. Add then into classpath too of your project.
As you can see that I've created two two package in my project. One for having all the beans and one having launcher class and route builder class. I've also created one folder with name target in the same project and respectively added there more folder with name input, output, failed folder.
Here, I've used FileComponent of the Camel for file processing. I've created one class with name TestCamelMain.java which act as a launcher of the Camel. Below is the code snippet of the same class.
TestCamelMain.java
------------------------------
public class TestCamelMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Enter: TestCamelMain.main");
CamelContext context = null;
try {
context = new DefaultCamelContext();
context.addRoutes(new IntegartionRoute());
context.start();
//Indefinitely wait
Object obj = new Object();
synchronized (obj) {
obj.wait();
}
//Thread.sleep(10000);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Error: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
try {
context.stop();
} catch (Exception e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("Exit: TestCamelMain.main");
}
}
-----------------------
Now we are going to create the route builder class which defined the flow of the incoming message. Here, I've created the class with name IntegartionRoute.java which extends RouteBuilder class. The code snippet as per below,
IntegartionRoute.java
------------------------
public class IntegartionRoute extends RouteBuilder{
@Override
public void configure() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Enter: IntegartionRoute.configure");
/**
* If we wanted to handle the any kind of exception occurred during the processing
* than we have to add the exception block first. This will capture the exception route the
* message to specified endpoint
* */
onException(Exception.class)
.maximumRedeliveries(0)
.process(new ExceptionProcessor())
.to("file:target/failed");
from("file:target/input")
.choice() //Here we can give the choice to the incoming document
.when(xpath("/order/product = 'gadget'"))
.process(new LoggingBean())
.bean(new TransformationBean(), "makeItUpperCase")
.to("file:target/output")
.otherwise()
.to("file:target/output1");
System.out.println("Exit: IntegartionRoute.configure");
}
}
------------------------------
In the above class I've defined the route of my incoming message. As I've stated that I've used FileComponent for receiving the file from target/input folder and after processing move to target/output folder by checking file content and by making file content to upercase.
Here, I've also handled the exception whenever occurred during the file processing in different component. In this case I've added one business logic to check the the file content whether it content contains the specific information or not by using xPath which is again Camel's component. If it do not contains the required information than we will send that file to target/output1 directory. If it contains than we will send it to the target/output directory. In between any error occurred than we will send that file to target/failed directory. Here, I've used Java DSL for defining the route.
I've considered the incoming file to be xml file. Below are the ExceptionProcessor, LoggingBean, TransformationBean which are used at different stages.
ExceptionProcessor.java
------------------------------
public class ExceptionProcessor implements Processor{
@Override
public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Enter: ExceptionProcessor.process");
Exception exception = (Exception) exchange.getProperty(Exchange.EXCEPTION_CAUGHT);
System.out.println("Error: " + exception.getMessage());
exception.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Exit: ExceptionProcessor.process");
}
}
------------------------
LoggingBean.java
------------------------
public class LoggingBean implements Processor{
@Override
public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Enter: LoggingBean.process");
System.out.println("Received Message Id: " + exchange.getIn().getMessageId());
System.out.println("Captured Data: " + exchange.getIn().getBody(String.class));
System.out.println("Exit: LoggingBean.process");
}
}
----------------------------
TransformationBean.java
----------------------------
public class TransformationBean {
public String makeItUpperCase(String body) {
System.out.println("Enter: TransformationBean.makeItUpperCase");
String transformedBody = body.toUpperCase();
System.out.println("TransformedBody : " + transformedBody);
System.out.println("Exit: TransformationBean.makeItUpperCase");
return transformedBody;
}
}
---------------------
Below are the xml file which I've used in processing,
---------------
sample.xml
---------------
<xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8">
<order>
<product>gadget</product>
<lineitems>
<item>cdplayer</item>
<qty>2</qty>
</lineitems>
<lineitems>
<item>ipod-nano</item>
<qty>1</qty>
</lineitems>
</order>
Congrats to you. You have learnt first lesson of Apache Camel.
Now by running TestCamelMain.class you can see the Camel is started. Now, for a magic you should put one file in target/input folder and check the respective folder and also see the console for the flow.
That's it. After reading this don't forgot to give your valuable feedback on the same. Your feedback might be useful to other and also encourage me to keep posting.
Cheers,
Ashish Mishra
Labels:
Apche Camel,
Camel Component,
Camel Context,
Camel Route,
DSL,
EIP,
Jboss Fuse,
MEP,
OSGi
Wednesday, September 24, 2014
HTML Parsing and Querying with JSoup
Now a days in web environment we have too much work with HTML pages.
If you have any requirement like parsing, querying or adding missing tags in html document than from my point of view JSoup is the answer for it.
Here, I am going to show some little work around HTML document with the help of JSoup utility.
Please download JSoup jar file from JSoup download page and add this into your projects lib directory.
Below is the code snippet for above discussion,
HTML File :
<!DOCTYPE html>
<body bgcolor="#FFFFFF" text="#000000">
<div align="center" id="mainDiv"><font size="6">Welcome to JSoup Test Demo</font>
</div>
<form name="testForm" method="post" action="controller_context_path">
<table width="90%" border="0" cellspacing="4" cellpadding="4">
<tr>
<td width="50%">
<div align="right">
User Id:
</div>
</td>
<td width="50%">
<div align="left">
<input type="text" name="userId" value="">
</div>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td width="50%">
<div align="right" id="div1">
Name:
</div>
</td>
<td width="50%">
<div align="left" id="div2">
<input type="text" name="orgId" value="">
</div>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td width="50%">
<div align="right"></div>
</td>
<td width="50%">
<div align="left" id="div3">
<input type="submit" name="Submit" value="Login">
</div>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
<p> </p>
</form>
</body>
</html>
-----------------------------------------------------------
Java Code:
Below is the code snippet to parse above document and querying to specific tag in HTML page,
File htmlFile = new File("HTML file path");
org.jsoup.nodes.Document document = Jsoup.parse(xslfile, "UTF-8");
This will create html document with all the tags. This will format whole html file if it broken or some tags which is not ended with their respective tag,
Now if we want body section of the html page than
Element body = document.body();
If we want to convert body element into string format than simply use body.toString() method of Element.
For traversing or querying across html document below is the code snippet.
Elements element = document.select("div.div1"); //tagName.id of the tag
This will returns all the div tags which have id div1 in html document.
Now querying exact document from the html document below is the code snippet,
Element element = document.select("div.div3").select("input[name$=Submit]").first();
This will returns the element of input type whose attribute name contains Submit text.
For in-depth querying pattern visit http://jsoup.org/cookbook/extracting-data/selector-syntax
This is things which i have mentioned here. You can visit http://jsoup.org for more information.
Here is the comparison of different HTML parser which will be useful in selecting the html parser which are currently available. Visit http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comparison_of_HTML_parsers
This might be helpful to you guys to initiate work related html document.
Please don't forgot to add your comment or feedback if you like this post or useful in any ways.
Cheers,
Ashish Mishra
If you have any requirement like parsing, querying or adding missing tags in html document than from my point of view JSoup is the answer for it.
Here, I am going to show some little work around HTML document with the help of JSoup utility.
Please download JSoup jar file from JSoup download page and add this into your projects lib directory.
Below is the code snippet for above discussion,
HTML File :
<!DOCTYPE html>
<body bgcolor="#FFFFFF" text="#000000">
<div align="center" id="mainDiv"><font size="6">Welcome to JSoup Test Demo</font>
</div>
<form name="testForm" method="post" action="controller_context_path">
<table width="90%" border="0" cellspacing="4" cellpadding="4">
<tr>
<td width="50%">
<div align="right">
User Id:
</div>
</td>
<td width="50%">
<div align="left">
<input type="text" name="userId" value="">
</div>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td width="50%">
<div align="right" id="div1">
Name:
</div>
</td>
<td width="50%">
<div align="left" id="div2">
<input type="text" name="orgId" value="">
</div>
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td width="50%">
<div align="right"></div>
</td>
<td width="50%">
<div align="left" id="div3">
<input type="submit" name="Submit" value="Login">
</div>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
<p> </p>
</form>
</body>
</html>
-----------------------------------------------------------
Java Code:
Below is the code snippet to parse above document and querying to specific tag in HTML page,
File htmlFile = new File("HTML file path");
org.jsoup.nodes.Document document = Jsoup.parse(xslfile, "UTF-8");
This will create html document with all the tags. This will format whole html file if it broken or some tags which is not ended with their respective tag,
Now if we want body section of the html page than
Element body = document.body();
If we want to convert body element into string format than simply use body.toString() method of Element.
For traversing or querying across html document below is the code snippet.
Elements element = document.select("div.div1"); //tagName.id of the tag
This will returns all the div tags which have id div1 in html document.
Now querying exact document from the html document below is the code snippet,
Element element = document.select("div.div3").select("input[name$=Submit]").first();
This will returns the element of input type whose attribute name contains Submit text.
For in-depth querying pattern visit http://jsoup.org/cookbook/extracting-data/selector-syntax
This is things which i have mentioned here. You can visit http://jsoup.org for more information.
Here is the comparison of different HTML parser which will be useful in selecting the html parser which are currently available. Visit http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comparison_of_HTML_parsers
This might be helpful to you guys to initiate work related html document.
Please don't forgot to add your comment or feedback if you like this post or useful in any ways.
Cheers,
Ashish Mishra
Saturday, August 2, 2014
Mostly asked HR interview questions with points
Here i have listed few key HR round interview questions with bullet point which are mostly asked. These questions are based on my personal experience. I think i should share this information with you and might be helpful to you when you are going to face HR round. Here i have listed only bullet points and not described in details.
Que 1: What is your strength?
Points to remember
Adaptability : Adjustable in any kind of environment situation to work
Hard Working : Very hard working towards work
Honest :
Flexibility : Can work any where and any place in any environment
Optimistic : Positive Attitude
Fast Decision Making : Fast decision making(Good decision) in any kind of situation and pressure
Persistence : Regular in work, work with dedication
Self Motivated : I am self motivated person
Example: I am honest, self motivated and hard working guy with positive attitude towards my carrer and life
Que 2: What is weakness?
Points to remember:
Straightforward : Strait forward attitude
Impatient : Impatient in work.
Sensitive
More Talkative
Trust people very quickly
I can't say no when someone ask for help
Take decisions very quickly
Get nervous when talk to stranger
To speak lie is difficult for me
I am bit lazy about which i am not interested
Example: I can't say no when someone ask for help and little bit lazy about which i am not interested
Note: Include only two-three points in weakness when facing real interview
Que 3: Why should i hire you?
Points to remember:
Share your knowledge
Work Experience
Skills Related to job
Career Goal
Example: With reference to my work experience, i satisfy all the requirement for this job. I am sincere with my work and would never let you down anyway. I promise you will never regret for the decision to appoint me in your organization.
Que 4: Tell me what you know about this company.
Points to remember:
Pre-study about the company in details
Do the background work about ongoing/upcoming projects
Know the names of owners and partners
Research about the current issues
Update your knowledge about their competitors
Example: It's one of the best growing company in India. The work environment of the company is very good. People feel proud to be part of the company as company provides full supports to their employees in professional front it has many branches across the world so i have good opportunity to show my talent.
Que 5: Why are looking for job change?
Points to remember
Thanks to previous organization
What you learn in your previous organization
Share your reason for job change
Relates to career goals
Example: I am thankful to my previous organization because i have learnt lot of things there. According to me changes are necessary for everyone to enhance skills, knowledge and for personal growth and financial growth. Your organization is the good platform where i can learn more.
Que 6: What are your salary requirements?
Points to remember
Should share their expected salary
Always say as per the company norms for the job
Example: I have 4 years of experience in IT. My current CTC is XXX Lac/yr salary has never been a big issue for me. Still i am expecting salary as company's norms as per my designation and my qualification and experience which can help me to maintain my standard of level of my personal and economical needs.
Que 7: What are your career goals?
Points to remember
Short term goal
Long term goal
Example: My short term goal is to get a job in reputed company where i can utilize my skills and improve my career path. My long term goal is to be in respectable position in that organization.
Que 8: Do you any questions to ask me?
Points to remember
Express thanks
Salary Structures
Job timings
Job Location
Overtime allowance
Training Period
Probation Period
Transport Facility
Example: Thank you for giving this opportunity. Sir I would like to know about the job timings and transport facility and what will be the job location and salary structure for this job?
Hope this will help you to crack HR round of interview. If you have any suggestion or feedback which help us than please share your opinion and feedback so i can add in the same.
Cheers,
Ashish Mishra
Que 1: What is your strength?
Points to remember
Adaptability : Adjustable in any kind of environment situation to work
Hard Working : Very hard working towards work
Honest :
Flexibility : Can work any where and any place in any environment
Optimistic : Positive Attitude
Fast Decision Making : Fast decision making(Good decision) in any kind of situation and pressure
Persistence : Regular in work, work with dedication
Self Motivated : I am self motivated person
Example: I am honest, self motivated and hard working guy with positive attitude towards my carrer and life
Que 2: What is weakness?
Points to remember:
Straightforward : Strait forward attitude
Impatient : Impatient in work.
Sensitive
More Talkative
Trust people very quickly
I can't say no when someone ask for help
Take decisions very quickly
Get nervous when talk to stranger
To speak lie is difficult for me
I am bit lazy about which i am not interested
Example: I can't say no when someone ask for help and little bit lazy about which i am not interested
Note: Include only two-three points in weakness when facing real interview
Que 3: Why should i hire you?
Points to remember:
Share your knowledge
Work Experience
Skills Related to job
Career Goal
Example: With reference to my work experience, i satisfy all the requirement for this job. I am sincere with my work and would never let you down anyway. I promise you will never regret for the decision to appoint me in your organization.
Que 4: Tell me what you know about this company.
Points to remember:
Pre-study about the company in details
Do the background work about ongoing/upcoming projects
Know the names of owners and partners
Research about the current issues
Update your knowledge about their competitors
Example: It's one of the best growing company in India. The work environment of the company is very good. People feel proud to be part of the company as company provides full supports to their employees in professional front it has many branches across the world so i have good opportunity to show my talent.
Que 5: Why are looking for job change?
Points to remember
Thanks to previous organization
What you learn in your previous organization
Share your reason for job change
Relates to career goals
Example: I am thankful to my previous organization because i have learnt lot of things there. According to me changes are necessary for everyone to enhance skills, knowledge and for personal growth and financial growth. Your organization is the good platform where i can learn more.
Que 6: What are your salary requirements?
Points to remember
Should share their expected salary
Always say as per the company norms for the job
Example: I have 4 years of experience in IT. My current CTC is XXX Lac/yr salary has never been a big issue for me. Still i am expecting salary as company's norms as per my designation and my qualification and experience which can help me to maintain my standard of level of my personal and economical needs.
Que 7: What are your career goals?
Points to remember
Short term goal
Long term goal
Example: My short term goal is to get a job in reputed company where i can utilize my skills and improve my career path. My long term goal is to be in respectable position in that organization.
Que 8: Do you any questions to ask me?
Points to remember
Express thanks
Salary Structures
Job timings
Job Location
Overtime allowance
Training Period
Probation Period
Transport Facility
Example: Thank you for giving this opportunity. Sir I would like to know about the job timings and transport facility and what will be the job location and salary structure for this job?
Hope this will help you to crack HR round of interview. If you have any suggestion or feedback which help us than please share your opinion and feedback so i can add in the same.
Cheers,
Ashish Mishra
Wednesday, January 29, 2014
DOM4J: Remove duplicate xml elements from xml
Today i will explain about handling duplicate xml elements of xml.
I think you are little bit aware with DOM4J API from Apache Foundation.
DOM4J API basically is for playing with XML. Sometime your facing the issue that how to get distinct element list from the given xml. To achive this we iterate whole document and get required list. But same thing can be achive by given DOM4J API.
You need to have a latest copy of dom4j.jar. You can easily download it from Sourceforge
Here i will show you the practical example of the same.
//XML Document
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<document>
<element>
<id>1</id>
</element>
<element>
<id>1</id>
</element>
<element>
<id>2</id>
</element>
<element>
<id>3</id>
</element>
<element>
<id>2</id>
</element>
<element>
<id>6</id>
</element>
<element>
<id>5</id>
</element>
<element>
<id>3</id>
</element>
<element>
<id>4</id>
</element>
<element>
<id>4</id>
</element>
</document>
Now create one class file and add below code snippet in your class
String xmlDoc = ""; //Add code which reads the xml input file from your file location
//Creating org.dom4j.Document objet from xml content
Document document = DocumentHelper.parseText(xmlDoc);
//Now creating distinct list from the created xml ducument with below code snippet
List<Node> nodes = document.selectNodes("//document/element", "id", true);
/*
* XPath for distinct element : "//document/element"
* Element name on which nodes will be compare: "id"
* Boolean flag which indicates to remove duplicate nodes or not.
**/
I think you are little bit aware with DOM4J API from Apache Foundation.
DOM4J API basically is for playing with XML. Sometime your facing the issue that how to get distinct element list from the given xml. To achive this we iterate whole document and get required list. But same thing can be achive by given DOM4J API.
You need to have a latest copy of dom4j.jar. You can easily download it from Sourceforge
Here i will show you the practical example of the same.
//XML Document
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<document>
<element>
<id>1</id>
</element>
<element>
<id>1</id>
</element>
<element>
<id>2</id>
</element>
<element>
<id>3</id>
</element>
<element>
<id>2</id>
</element>
<element>
<id>6</id>
</element>
<element>
<id>5</id>
</element>
<element>
<id>3</id>
</element>
<element>
<id>4</id>
</element>
<element>
<id>4</id>
</element>
</document>
Now create one class file and add below code snippet in your class
String xmlDoc = ""; //Add code which reads the xml input file from your file location
//Creating org.dom4j.Document objet from xml content
Document document = DocumentHelper.parseText(xmlDoc);
//Now creating distinct list from the created xml ducument with below code snippet
List<Node> nodes = document.selectNodes("//document/element", "id", true);
/*
* XPath for distinct element : "//document/element"
* Element name on which nodes will be compare: "id"
* Boolean flag which indicates to remove duplicate nodes or not.
**/
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)