Here, I'm going to explain basic things of Apache Camel which is an open source project from Apache Foundation. At the end we will see the simple example which demonstrate the FileComponent of Apche Camel.
To go further I assumed that you have enough knowledge of EIP(Enterprise Integration Patterns), MEP(Message Exchange Patterns), DSL(Domain Specific Languages), ESB, etc. It is advised to have basic information of above mentioned terms before you read further.
Now a days data becoming crucial things in the Cyber World among all the companies. To exchange the data between them is more crucial as each company has their own system to handle this data. It is important to have technology which fills this gap in such a way that exchange of data among companies accurately, efficiently, speedily, reliably, securely and off course easily. There are many open source solutions available to fill this gap. But I found Apache Camel is most preferable open source solution for integrating different systems to exchange the data in a different format. I became a camel lover since when I started using it and off-course because it is written in Java.
Now, I think this is enough for you about why Apache Camel is useful. Let's start with the Apache Camel architecture.
To go further I assumed that you have enough knowledge of EIP(Enterprise Integration Patterns), MEP(Message Exchange Patterns), DSL(Domain Specific Languages), ESB, etc. It is advised to have basic information of above mentioned terms before you read further.
Now a days data becoming crucial things in the Cyber World among all the companies. To exchange the data between them is more crucial as each company has their own system to handle this data. It is important to have technology which fills this gap in such a way that exchange of data among companies accurately, efficiently, speedily, reliably, securely and off course easily. There are many open source solutions available to fill this gap. But I found Apache Camel is most preferable open source solution for integrating different systems to exchange the data in a different format. I became a camel lover since when I started using it and off-course because it is written in Java.
Now, I think this is enough for you about why Apache Camel is useful. Let's start with the Apache Camel architecture.
Now let's see the key concept or components which make Apache Camel a powerful integration and routing framework among all the available in the same category.
- Camel Context: Camel Context is the heart of the Camel Framework. It's runtime environment where different entity communicate with each other. For more you can see the lifecyle of CamelContext in detail
- Camel Endpoints: Camel Endpoints are nothing but the Message Endpoints which is based on EIP by using Endpoint interface. Camle can receive messages from Endpoints or send messages to the Endpoints. You can read more on EIP by visiting this http://www.enterpriseintegrationpatterns.com
- Camel Processors: Processors are the again key entity in camel which is associated with processing of incoming messages from Endpoints. For more you can visit http://camel.apache.org/processor.html
- Camel Components: Camel Components defined the Endpoint in message lifecyle in camel. There are more than 80 components available in the camel. You can refer them on official camel website. http://camel.apache.org/components.html
- Camel Route: Camel Route are the flow of the message. How it process in camel. It has two endpoints associated with it and respectively Camel component as well. Camel route also having the filter, interceptor, validator, converter which defined the flow of the message. We can create a route via DSL. There are different DSL available which defined the route of the message. Most commonly used are Spring DSL, Java DSL. You can read more on that by your own as it's a very huge topic and we are not going elaborate them over here.
Now, I'm winding up theoretical part as you can read whenever you want from the net. I knew that you are quite interested in the programming. :D :D :D
So, Let's begin that. First you need to download the Apache Camel from the official site. You can download form here.
I will be surprised if you don't have java installed on your machine and you are not using any of the popular IDE for doing programming. If you do not have java than please make java available on your machine.
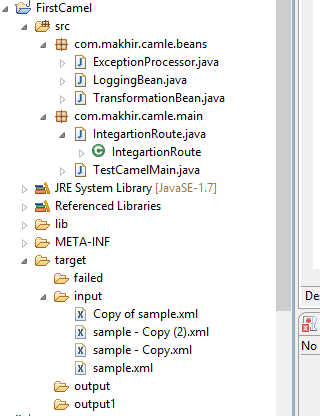
Now, create on java project. Here, I've used Eclipse IDE for my stuffs. Below is the directory structure.
Add the required jar in the lib folder of your project from the downloaded Apache Camel zip file after extraction on you local drive. Add then into classpath too of your project.
As you can see that I've created two two package in my project. One for having all the beans and one having launcher class and route builder class. I've also created one folder with name target in the same project and respectively added there more folder with name input, output, failed folder.
Here, I've used FileComponent of the Camel for file processing. I've created one class with name TestCamelMain.java which act as a launcher of the Camel. Below is the code snippet of the same class.
TestCamelMain.java
------------------------------
public class TestCamelMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Enter: TestCamelMain.main");
CamelContext context = null;
try {
context = new DefaultCamelContext();
context.addRoutes(new IntegartionRoute());
context.start();
//Indefinitely wait
Object obj = new Object();
synchronized (obj) {
obj.wait();
}
//Thread.sleep(10000);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Error: " + e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
try {
context.stop();
} catch (Exception e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("Exit: TestCamelMain.main");
}
}
-----------------------
Now we are going to create the route builder class which defined the flow of the incoming message. Here, I've created the class with name IntegartionRoute.java which extends RouteBuilder class. The code snippet as per below,
IntegartionRoute.java
------------------------
public class IntegartionRoute extends RouteBuilder{
@Override
public void configure() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Enter: IntegartionRoute.configure");
/**
* If we wanted to handle the any kind of exception occurred during the processing
* than we have to add the exception block first. This will capture the exception route the
* message to specified endpoint
* */
onException(Exception.class)
.maximumRedeliveries(0)
.process(new ExceptionProcessor())
.to("file:target/failed");
from("file:target/input")
.choice() //Here we can give the choice to the incoming document
.when(xpath("/order/product = 'gadget'"))
.process(new LoggingBean())
.bean(new TransformationBean(), "makeItUpperCase")
.to("file:target/output")
.otherwise()
.to("file:target/output1");
System.out.println("Exit: IntegartionRoute.configure");
}
}
------------------------------
In the above class I've defined the route of my incoming message. As I've stated that I've used FileComponent for receiving the file from target/input folder and after processing move to target/output folder by checking file content and by making file content to upercase.
Here, I've also handled the exception whenever occurred during the file processing in different component. In this case I've added one business logic to check the the file content whether it content contains the specific information or not by using xPath which is again Camel's component. If it do not contains the required information than we will send that file to target/output1 directory. If it contains than we will send it to the target/output directory. In between any error occurred than we will send that file to target/failed directory. Here, I've used Java DSL for defining the route.
I've considered the incoming file to be xml file. Below are the ExceptionProcessor, LoggingBean, TransformationBean which are used at different stages.
ExceptionProcessor.java
------------------------------
public class ExceptionProcessor implements Processor{
@Override
public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Enter: ExceptionProcessor.process");
Exception exception = (Exception) exchange.getProperty(Exchange.EXCEPTION_CAUGHT);
System.out.println("Error: " + exception.getMessage());
exception.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Exit: ExceptionProcessor.process");
}
}
------------------------
LoggingBean.java
------------------------
public class LoggingBean implements Processor{
@Override
public void process(Exchange exchange) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Enter: LoggingBean.process");
System.out.println("Received Message Id: " + exchange.getIn().getMessageId());
System.out.println("Captured Data: " + exchange.getIn().getBody(String.class));
System.out.println("Exit: LoggingBean.process");
}
}
----------------------------
TransformationBean.java
----------------------------
public class TransformationBean {
public String makeItUpperCase(String body) {
System.out.println("Enter: TransformationBean.makeItUpperCase");
String transformedBody = body.toUpperCase();
System.out.println("TransformedBody : " + transformedBody);
System.out.println("Exit: TransformationBean.makeItUpperCase");
return transformedBody;
}
}
---------------------
Below are the xml file which I've used in processing,
---------------
sample.xml
---------------
<xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8">
<order>
<product>gadget</product>
<lineitems>
<item>cdplayer</item>
<qty>2</qty>
</lineitems>
<lineitems>
<item>ipod-nano</item>
<qty>1</qty>
</lineitems>
</order>
Congrats to you. You have learnt first lesson of Apache Camel.
Now by running TestCamelMain.class you can see the Camel is started. Now, for a magic you should put one file in target/input folder and check the respective folder and also see the console for the flow.
That's it. After reading this don't forgot to give your valuable feedback on the same. Your feedback might be useful to other and also encourage me to keep posting.
Cheers,
Ashish Mishra